Nods Gambling Screen
- Nods Gambling Screen On Mac
- Nods Gambling Screen Game
- Nods Gambling Screen
- Nods Gambling Screen Keyboard Shortcut
- Nods Gambling Screen App
Brief Biosocial Gambling Screen (BBGS)
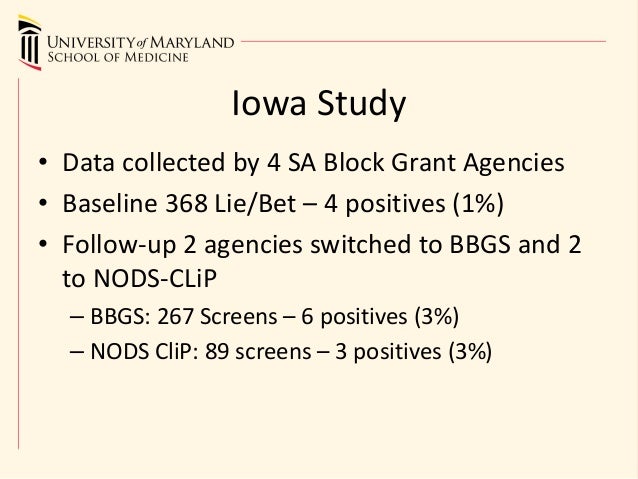
To describe and evaluate tests of the performance of the NODS–CLiP, an efficient standardized diagnostic interview instrument for adult pathological and problem gambling.
Screen for Gambling Problems (NODS) 34. Poll Question #3 The two themes of the Lie/Bet Questionnaire are losing control and lying. Suicide & Money. Apr 26, 2017 Review research and evidence based rationale for problem gambling screening Describe evidence based brief problem gambling screens and their effectiveness in actual clinical settings Present recommendations for best clinical practices for effective screening and initiating conversation around the impact of gambling on recovery 1 2 3. The NORC Diagnostic Screen for Gambling Problems—Revised INTERVIEWER: For each question asked, circle YES or NO. When interview is complete, for questions for which R said YES, mark the corresponding box in the right-hand margin, ignoring items that do not have a corresponding box.
The Brief Biosocial Gambling Screen (BBGS) is a 3-item survey designed to help people decide on their own whether to seek a formal evaluation of their gambling behavior. The BBGS is based on the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV) criteria for pathological gambling.
DSM-5 Gambling Disorder Criteria
The American Psychiatric Association provides guidelines used for gambling disorders in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5). For more information on the DSM-5, please visit http://www.dsm5.org/.
NORC Diagnostic Screen for Gambling Problems-Self Administered (NODS-SA)
The NODS-SA is self-assessment version of the NODS (the NORC Diagnostic Screen for Gambling Disorders). It was designed to assist individuals in evaluating whether to modify or seek help for their gambling behavior. The NODS is based on the APA’s DSM-IV criteria for pathological gambling.
Please answer the following 10 yes/no questions honestly:
*REMINDER: this self-assessment will help you figure out if there is a problem, but only a professional can diagnose if it is a gambling problem, a different problem, or both.
If you answered yes to one or more of the above questions, you should seek help.
Assessment Tools
Nods Gambling Screen On Mac
Assessment Tools
Nods Gambling Screen Game
Gerstein, Dean et al. The NORC DSM-IV Screen for Gambling (the NODS):
Gambling Impact and Behavior Study: report to the National Gambling Impact Study Commission. Submitted on April 1, 1999. Chicago: National Opinion Research Center.
This assessment tool was designed in the 1999 Gambling Impact and Behavior Study. A structured interview used to determine the prevalence of problem gambling in a population. The NODS consists of 17 questions intended to reflect the DSM-IV criteria It was developed and tested on non-clinical population, and is based upon DSM-IV criteria. Respondents to the NODS are classified as non-gamblers, low-risk, at risk, problem,
and pathological.
Lesieur, Henry & Blume, Sheila. (1987). The South Oaks Gambling Screen: A new instrument for the identification of path-ological gamblers. In the American Journal of Psychiatry. Sep; Vol 144(9): 1184-1188.
The SOGS was originally developed to screen for gambling problems in clinical populations and is a scientifically reliable and valid instrument of 20 items based on DSM III criteria for pathological gambling. It has been the most widely used assessment screen for problem gambling by researchers and counsellors, though it has not been specifically validated for that use.

Nods Gambling Screen
Shaffer, H.J., LaBrie, R., Scanlan, M. & Cummings, T.N. (1994). Pathological Gambling Among Adolescents: Massachusetts Gambling Screen (MAGS). Journal of Gambling Studies, 10 (4), 339-362.
The MAGS is a clinical tool that can be administered in a 5 to10 minute survey or interview. The MAGS presents an index of non-pathological (NPLG) and pathological (PLG) gambling based upon the criteria of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV (DSM-IV). Outcomes also outline the prevalence of a variety of social and emotional problems associated with adolescent gambling.


Nods Gambling Screen Keyboard Shortcut
Turner, Nigel and Horbay, Roger. (1998). Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) Gambling Screen. Unpublished.
The CAMH Gambling Screen is primarily based on the SOGS and contains 7 items in total. The first 5 were adapted directly from the SOGS. Another item was developed by Turner and Horbay; and the final item determines the frequency of problem gambling. This tool was essentially developed to screen for problem gamblers, to determine if problem gambling is an issue and if there is a need for treatment.
Nods Gambling Screen App
Winters, Ken C., Stinchfield, Randy & Fulkerson, Jayne. (1993). South Oaks Gambling Screen-Revised Adolescent (SOGS-RA): Patterns and characteristics of adolescent gambling. Journal-of-Gambling-Studies, 9 (4), 371-386.
The SOGS for adults was revised for adolescents by changing the wording
to draw on adolescent lingo and relevant situations.